The realm of online privacy, security, and tracking can be intricate. It is crucial to comprehend that even if you believe you have taken all the necessary precautions, you can still be tracked and profiled while using your iPhone or other Apple devices.
Tracking, however, is not always malevolent. On the contrary, it is an essential aspect of online life, enabling personalized ads and supporting some free services. The harm occurs when tracking is done irresponsibly or by malicious entities. Let’s delve into how and why you are tracked online, how to ascertain if your iPhone is being tracked, and the settings available in your iPhone and Safari browser to take charge of how you are tracked.
How Online Tracking Works
Most individuals are likely somewhat familiar with cookies. Cookies allow a website to recognize you as a visitor, offer specific services associated with the website, and remember your login credentials. Additionally, cookies are utilized to deliver targeted ads — not ideal for someone trying to cut back on expenses or buying a surprise gift for a spouse, where ads could spoil the surprise.
Cookies are also utilized to track the sites you visit and your activities on those sites. Since cookies are stored on your device, you have the option to delete or clear them. Fortunately, Apple provides sophisticated settings that empower users to manage cookies. You can learn all about blocking and deleting cookies on your iPhone here.
This leads us to a more ambiguous tracking technique known as device fingerprinting. Advertisers, apps, and websites employ this technique to identify your device and de-anonymize your profile. It involves collecting a blend of details from you, even if cookies are disabled. For instance, device fingerprinting can often discern your device type, battery health, browser type and version, operating system, IP address and network information, GPU/CPU and memory attributes, installed fonts, screen resolution, scroll speed, enabled plugins, downloaded apps, and more. Similar to the lines on your fingers, these individual data points may not be unique, but when combined, they distinguish you from other users, enabling tracking of your activities across the web.
Like cookies, device fingerprinting serves both legitimate and shady purposes. For instance, banks utilize it for fraud prevention and device authentication, such as identifying unusual or unrecognized devices associated with your account. Simultaneously, it is used for cross-site tracking, targeted advertising, and even to bypass certain privacy tools like VPNs.
Are You Under Surveillance?
As mentioned earlier, it is nearly impossible to evade all tracking from device fingerprinting since the collected data is derived from device properties rather than a stored identifier like a cookie.
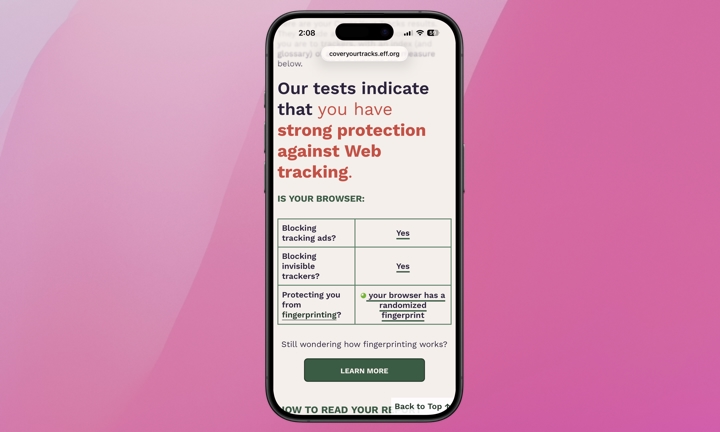
If you wish to assess how effectively your current settings shield you from device tracking, you can visit Cover Your Tracks, a complimentary tool from the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF), a nonprofit organization dedicated to safeguarding digital privacy and free speech. Subsequently, test the browser you predominantly use on your iPhone.
Hopefully, you will receive a message stating that “your browser has a randomized fingerprint.” According to Cover Your Tracks, “randomization offers robust protection against tracking companies attempting to fingerprint your browser.”
You will likely also see a message indicating that your browser “…has a fingerprint that conveys at least X bits of identifying information.” Additionally, there is a link to delve deeper into the measurements used to generate your results.
iPhone Settings to Reduce Device Fingerprinting
If you aim to minimize device fingerprinting across websites on your iPhone, we recommend utilizing Safari over other browsers like Chrome. Apart from being integrated with Apple’s OS and the broader Apple ecosystem, which collectively mitigate data-sharing risks, Safari incorporates features like Intelligent Tracking Prevention (ITP) and Fingerprinting Defense, presenting trackers with a simplified version of your configuration, making your iPhone less distinguishable.
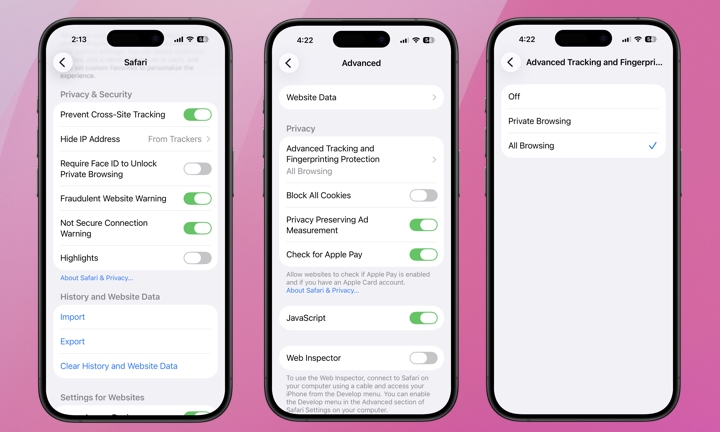
When using Safari, access your Safari settings to activate Prevent Cross-Site Tracking and conceal your IP address from trackers:
- Launch the Settings app on your iPhone
- If you are using iOS 18 or later, scroll to the bottom and select Apps (users on iOS 17 or earlier versions can skip this step).
- Locate and choose Safari.
- Scroll down to Privacy & Security.
- Ensure that Prevent Cross-Site Tracking is enabled.
- Directly below Prevent Cross-Site Tracking , you will find Hide IP Address. Tap it and confirm that From Trackers is selected.
You should also enable Advanced Tracking and Fingerprinting Protection:
- Scroll to the bottom of the primary Safari settings menu (from the aforementioned steps) and choose Advanced.
- Beneath Privacy, tap on Advanced Tracking and Fingerprinting Protection
- Select All Browsing for the most advanced protection.
Additionally, consider activating iCloud Private Relay. This offers greater anonymity than most traditional VPNs, provided you are using Safari, and is already included if you have any amount of iCloud storage. Some websites may not permit browsing with iCloud Private Relay. In such cases, you can temporarily authorize the website to view your IP address.
A wireless network or service may also be incompatible with iCloud Private Relay, in which case you can disable it for that specific cellular or Wi-Fi network. If this seems cumbersome, you are not obligated to use it, but at least you are aware of how to do so.
Here is how to enable iCloud Private Relay:
- Open the Settings app on your iPhone.
- Select your name at the top.
- Choose iCloud.
- Scroll down, select Private Relay, and toggle it on.
Another suggestion, aside from using Safari, is to utilize Private Tabs when shopping or researching products. This should significantly reduce your exposure to ads related to your shopping and product research.
While these Safari settings safeguard your web browsing, they do not halt apps from tracking you. Apple offers another feature known as App Tracking Transparency, which you can manage under Settings > Privacy & Security > Tracking, displaying which apps have requested permission to track your activity across other companies’ apps and websites — enabling you to disable the ones you do not wish to track you. Apple cannot entirely prevent third-party apps from employing more advanced techniques like digital fingerprinting, but this setting complicates their efforts. You can also obtain an App Privacy Report to monitor the activities of third-party apps.
Apple goes to great lengths to ensure users’ privacy and security across various levels. As a user, you bear the responsibility of understanding the available features and their limitations. If you aspire to restrict tracking of your online activities, this guide should serve as a starting point.
global $wp;
. ‘/’;
?>